What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
Carbon Capture and Storage is the method of collecting and storing carbon dioxide emissions, safely and securely.
Carbon Capture and Storage, or CCS, is the method of capturing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, and safely and securely storing it in geological formations deep underground. This proven technology ensures that carbon dioxide captured from industrial processes and facilities does not reach the atmosphere, and therefore does not contribute to global climate change.
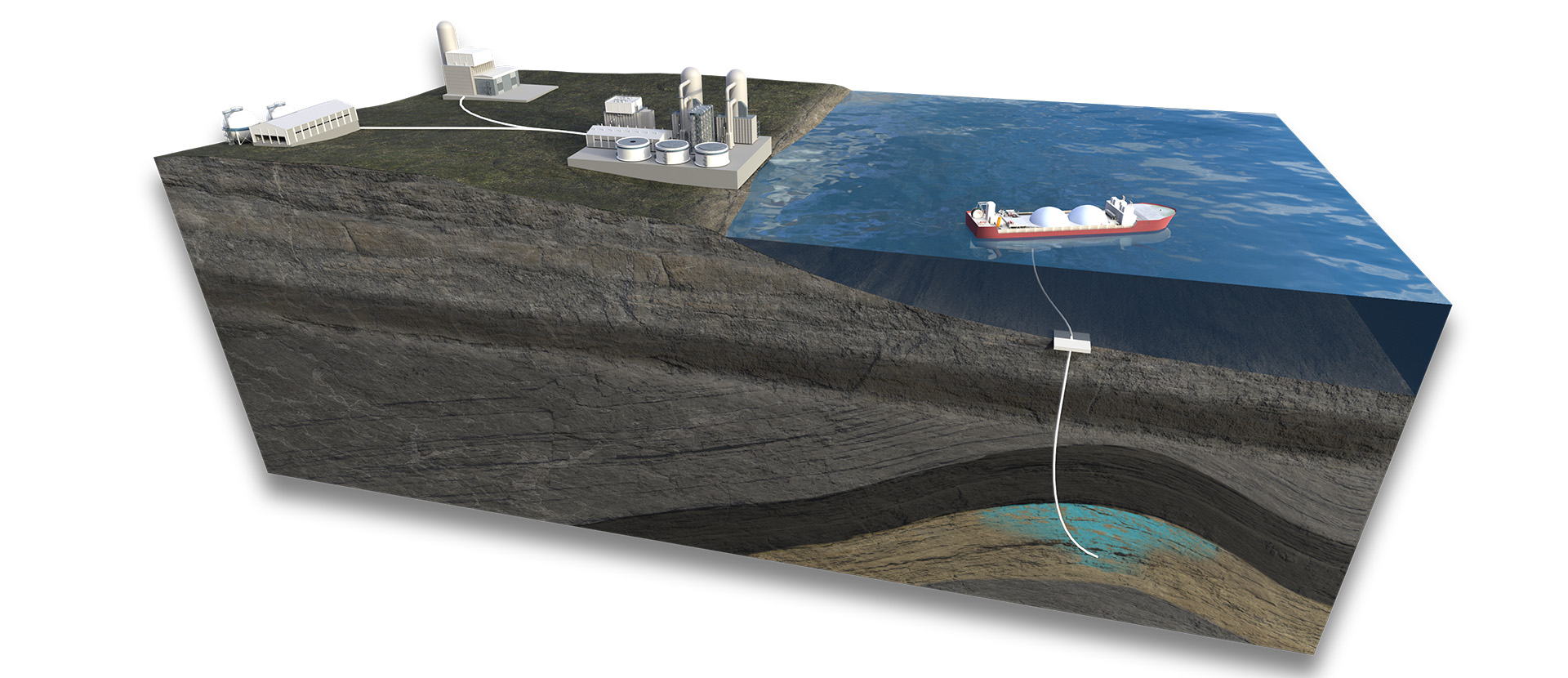
There are generally three parts in a carbon capture and storage project.
Capture
Carbon dioxide emissions are captured at industrial facilities and processed to separate carbon dioxide from other gases that may be generated. The capture technology that is used is dependent upon the industrial process and type of facility.
Transport
Geological storage sites are rarely located close to emissions sites, so captured carbon dioxide needs to be transported. There are various methods of transportation utilised, dependent upon the location of the emissions sources and whether or not the storage site is located onshore or offshore. Captured carbon dioxide may be transported via pipeline, via road, or via dedicated liquid CO2 transport vessels.
Storage
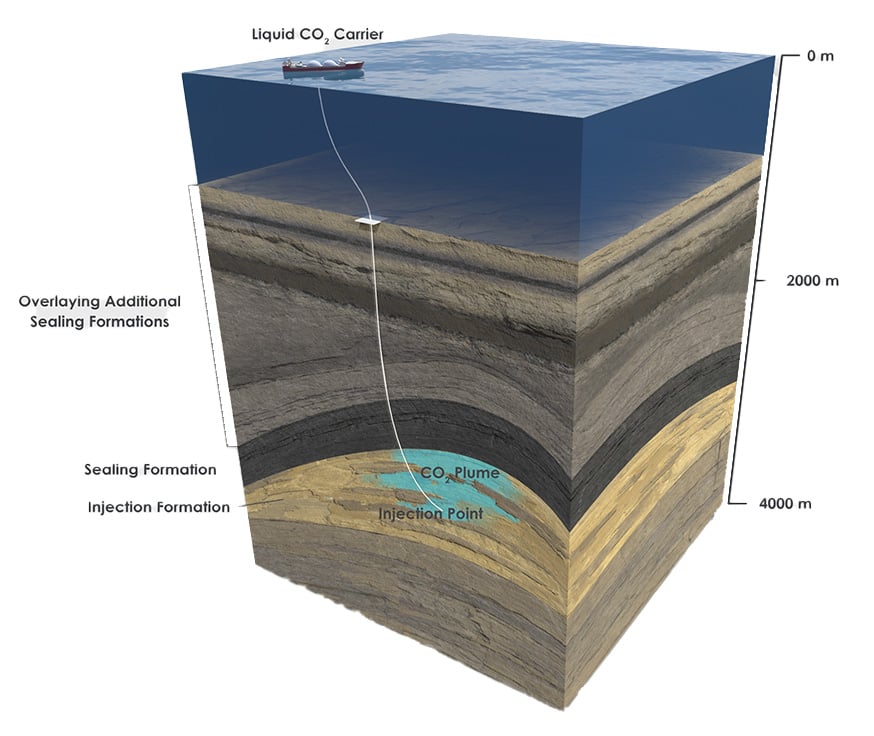
Captured carbon dioxide is injected deep underground into geological formations that are suitable for the safe and secure storage of carbon dioxide. Sequestration sites are carefully selected and subjected to rigorous screening procedures to ensure that they are able to safely and securely store carbon dioxide. The process of injection involves pumping liquid carbon dioxide into the geological formation, which is generally kilometres under the surface. This technology has been used around the world for decades and is a safe, secure and proven technology for carbon management and will be critical in securing the World’s net-zero status.